What is the Type 1 Diabetes Honeymoon Phase?
The honeymoon phase in type 1 diabetes is a period that occurs after the initial diagnosis and treatment of the condition. It’s a unique stage where individuals experience a temporary reprieve from the intense insulin dependence typically associated with type 1 diabetes. During this phase, the pancreas, though damaged, may still produce some insulin, leading to lower insulin requirements and more stable blood sugar levels. Understanding the honeymoon phase is crucial for both newly diagnosed patients and their caregivers, as it influences treatment strategies and expectations. It is a time of adjustment and careful management.
Understanding the Initial Diagnosis
The initial diagnosis of type 1 diabetes marks the beginning of a lifelong journey. The body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells (beta cells) in the pancreas. This autoimmune response results in an inability to produce sufficient insulin, which is essential for regulating blood glucose. The diagnosis often comes after experiencing symptoms such as excessive thirst, frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, and fatigue. The diagnostic process involves blood tests to measure blood glucose levels and assess the presence of autoantibodies. This is a time of significant adjustment, requiring education and the implementation of a new lifestyle that includes insulin therapy and careful monitoring of blood glucose.
The Body’s Autoimmune Attack
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease where the body’s immune system, which normally fights off infections, attacks and destroys its own beta cells in the pancreas. This autoimmune response is not fully understood, but it is believed to be triggered by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. The destruction of beta cells leads to a deficiency of insulin, a hormone crucial for glucose metabolism. This process occurs gradually, often over months or even years, before symptoms become noticeable. The body’s inability to produce insulin results in elevated blood sugar levels, which, if left untreated, can lead to serious health complications. Managing the autoimmune response is a key aspect of type 1 diabetes management.
What Happens During the Honeymoon Phase?
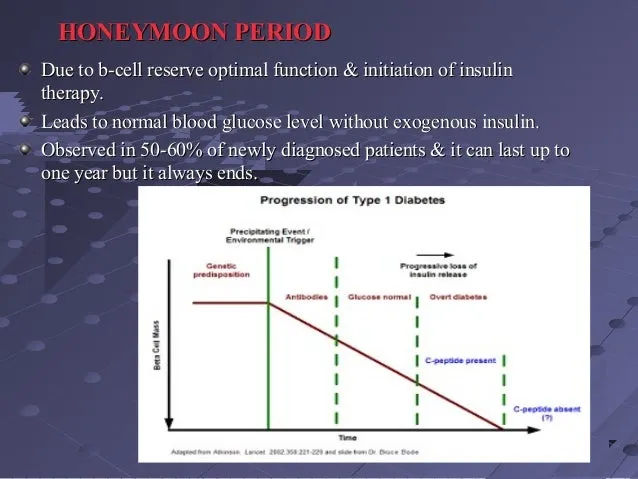
During the honeymoon phase, the pancreas, though damaged by the autoimmune attack, may still produce some insulin. This residual insulin production, combined with the initial insulin therapy, can lead to a period of relatively stable blood sugar levels. The individual may experience lower insulin requirements and fewer fluctuations in blood glucose. It’s important to note that the honeymoon phase is temporary, and the pancreas gradually loses its ability to produce insulin. This phase can last for weeks, months, or sometimes even years, but eventually, insulin therapy will become essential to manage blood sugar levels. The duration and intensity of the honeymoon phase vary greatly from person to person.
Temporary Insulin Production
The hallmark of the honeymoon phase is the temporary preservation of some insulin production. This residual insulin, secreted by the remaining beta cells, helps the body process glucose more efficiently. Consequently, individuals may need lower doses of insulin injections or insulin pump settings. This period offers a respite from the intensive insulin management typically required in type 1 diabetes. The degree of insulin production varies; some individuals may experience significant insulin release, while others may have minimal residual function. Itu2019s important to monitor blood sugar levels closely during this period and adjust insulin dosages as needed, under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
How Long Does the Honeymoon Phase Last?

The duration of the honeymoon phase varies significantly among individuals. It can last from a few weeks to several months, and in rare cases, up to a year or more. Several factors influence the duration, including age at diagnosis, the initial severity of the disease, and the treatment regimen. Generally, the honeymoon phase tends to be shorter in younger individuals. Itu2019s essential to understand that the honeymoon phase is temporary, and the individual will eventually require more insulin as the remaining beta cells are gradually destroyed. Regular monitoring and proactive adjustments to insulin therapy are crucial to manage blood sugar levels effectively during this phase.
Factors Influencing Honeymoon Phase Duration
Several factors influence the duration of the honeymoon phase. These include the age at which type 1 diabetes is diagnosed, with younger individuals often experiencing a shorter honeymoon phase. The initial severity of the disease also plays a role, as those with less severe initial symptoms might have a longer honeymoon period. The treatment regimen, particularly the timing and dosage of insulin, can influence how long the honeymoon phase lasts. Additionally, the level of adherence to the treatment plan, including diet, exercise, and blood sugar monitoring, can impact the duration. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and closely following medical advice can potentially extend the honeymoon phase and contribute to better overall diabetes management.
Symptoms and Signs to Watch Out For
During the honeymoon phase, it’s essential to monitor for signs that the phase is ending. These include increased blood sugar levels, increased thirst and urination, and a return of fatigue or unexplained weight loss. Insulin requirements may begin to increase, and there might be more frequent blood sugar fluctuations. Regular blood glucose monitoring is crucial to detect these changes early. Be aware of the symptoms of hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia. Recognizing the signs that the honeymoon phase is ending allows for timely adjustments to the insulin dosage, diet, and exercise regimen. Early detection is critical for maintaining good blood sugar control and preventing complications.
Blood Sugar Fluctuations
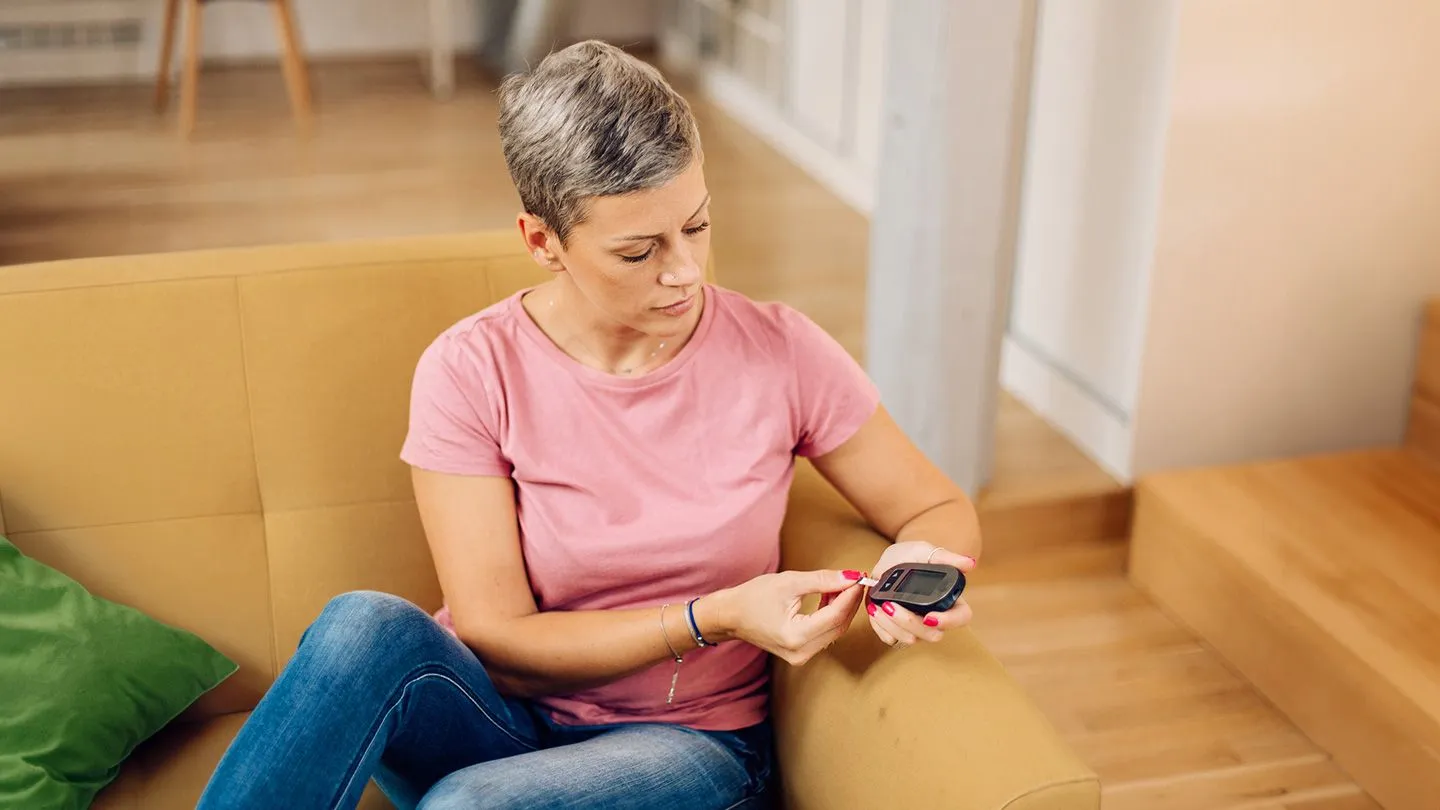

Blood sugar fluctuations are a common challenge during the honeymoon phase. As the remaining beta cells gradually decline, the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar becomes less effective. Individuals may experience both hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) and hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). These fluctuations can be influenced by various factors, including food intake, physical activity, stress, and illness. Careful monitoring of blood glucose levels is crucial to manage these fluctuations effectively. Regular blood glucose checks, along with adjustments to insulin dosages and dietary modifications, are essential to minimize extreme blood sugar swings and maintain optimal control.
Hypoglycemia and Hyperglycemia
Both hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) can occur during the honeymoon phase. Hypoglycemia can result from too much insulin, delayed meals, or increased physical activity. Symptoms include shakiness, sweating, confusion, and, in severe cases, loss of consciousness. Hyperglycemia, on the other hand, can be caused by too little insulin, illness, or consuming too many carbohydrates. Symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, and fatigue. Knowing the symptoms of both hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia is crucial for prompt action. Regularly monitoring blood sugar levels, carrying a source of fast-acting carbohydrates for low blood sugar, and adjusting insulin dosages as needed are important strategies to manage these conditions.
Managing Blood Sugar Levels
Managing blood sugar levels during the honeymoon phase requires a proactive approach. Regular blood glucose monitoring is essential, often before meals and at bedtime, to track blood sugar patterns. Insulin dosages may need to be adjusted frequently in response to blood sugar readings and other factors. Working closely with a diabetes healthcare team, including a doctor, nurse, and dietitian, is vital for personalized guidance. They can help tailor an insulin regimen, provide dietary advice, and offer support to navigate the challenges of this phase. Additionally, learning to recognize the signs and symptoms of high and low blood sugar is critical for timely intervention and adjustments to maintain optimal blood sugar control.
Importance of Regular Monitoring
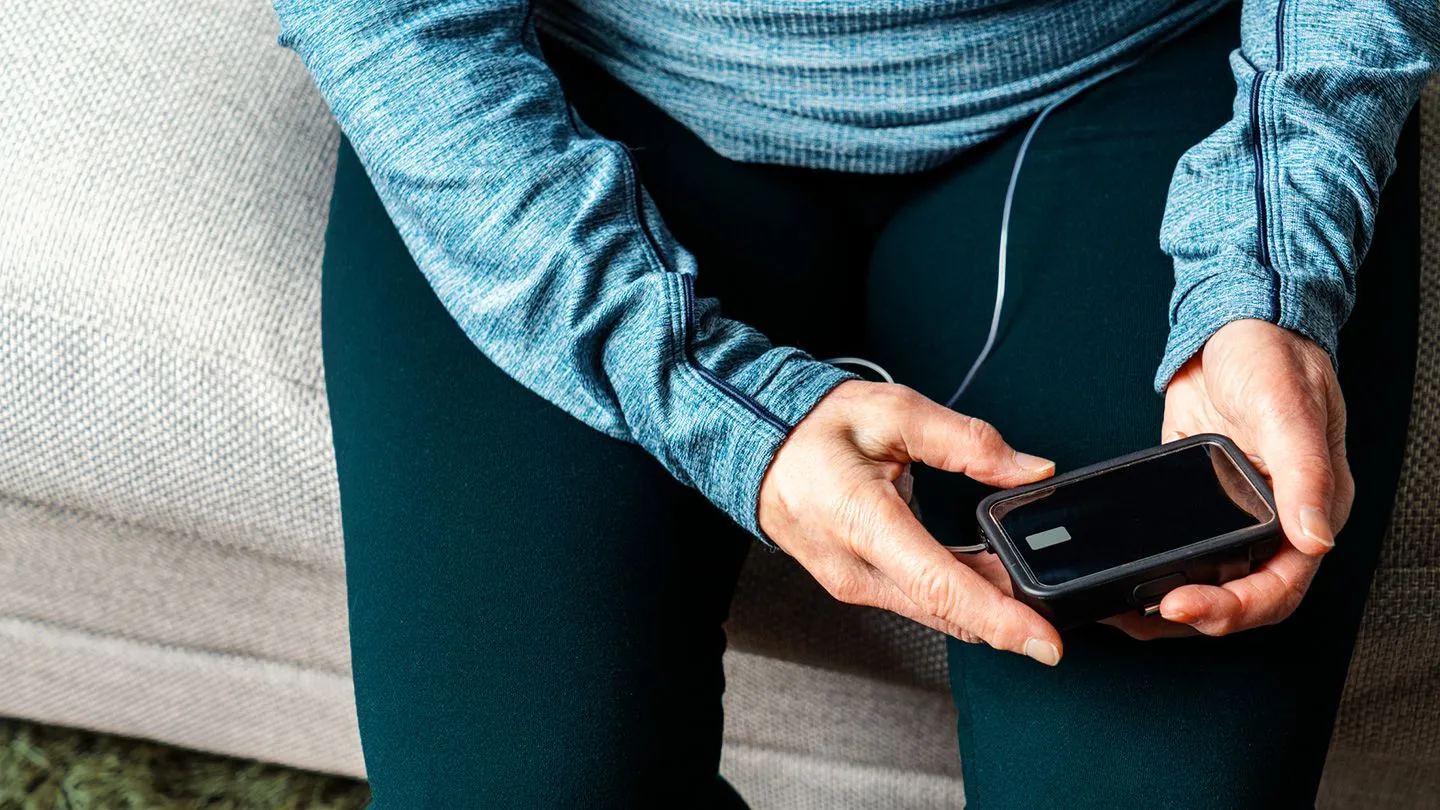

Regular blood glucose monitoring is a cornerstone of effective diabetes management, especially during the honeymoon phase. Monitoring should be done several times a day, including before meals, after meals, and at bedtime. The frequency of monitoring may vary depending on individual needs and the advice of the healthcare team. Regular monitoring provides valuable insights into how food, exercise, and insulin affect blood sugar levels. This information enables individuals to adjust insulin dosages, meal planning, and physical activity to maintain blood sugar within the target range. Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices can also be used to provide real-time blood sugar data and alert individuals to high or low blood sugar levels.
Dietary Recommendations
Diet plays a vital role in managing blood sugar levels during the honeymoon phase. A balanced diet that includes a consistent intake of carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats is recommended. Carbohydrate counting is often used to determine the amount of insulin needed for meals. Focus on consuming whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins. Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive amounts of saturated and trans fats. It’s important to work with a registered dietitian to create a personalized meal plan that takes into account individual needs, preferences, and insulin requirements. Regular meal times and portion control are also important to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Carbohydrate Counting
Carbohydrate counting is an essential tool for managing blood sugar levels, especially during the honeymoon phase. It involves tracking the amount of carbohydrates consumed in each meal and adjusting insulin dosages accordingly. Carbohydrates have the most significant impact on blood sugar levels, so accurately counting them is crucial for effective insulin management. Individuals can learn to read food labels, estimate carbohydrate content in meals, and make informed decisions about insulin doses. By mastering carbohydrate counting, individuals can better match their insulin intake to their food intake, leading to more stable blood sugar levels. It is important to be trained by a certified diabetes educator or a registered dietitian for accuracy.
Exercise and Physical Activity

Regular exercise is beneficial for overall health and plays a significant role in managing blood sugar levels during the honeymoon phase. Physical activity can improve insulin sensitivity, which means the body requires less insulin to process glucose. Exercise can also help with weight management, improve cardiovascular health, and reduce the risk of long-term diabetes complications. It’s important to monitor blood sugar levels before, during, and after exercise to understand how physical activity affects blood glucose. Depending on the type and intensity of exercise, individuals may need to adjust their insulin dosages or consume snacks to prevent hypoglycemia. Consulting with a healthcare professional to create an exercise plan that is safe and effective is advised.
Insulin Dosage Adjustment
Insulin dosage adjustments are a critical part of managing blood sugar levels during the honeymoon phase. As the pancreas’s ability to produce insulin changes, the insulin requirements fluctuate. Regular blood sugar monitoring provides the data needed to make informed adjustments. Insulin dosages may need to be decreased during the honeymoon phase, or increased if blood sugars begin to rise. These adjustments should always be made under the guidance of a healthcare professional. They can help to interpret blood sugar patterns and recommend appropriate changes. It’s essential to keep a detailed log of blood sugar readings, insulin doses, and food intake to identify trends and make more precise adjustments.
The Role of Healthcare Professionals
Healthcare professionals, including endocrinologists, diabetes educators, and registered dietitians, play a crucial role in managing type 1 diabetes, especially during the honeymoon phase. They provide essential education, support, and guidance to individuals with diabetes and their families. Healthcare professionals help individuals understand the disease, monitor blood sugar levels, administer insulin, make dietary adjustments, and manage exercise. They work collaboratively to create a personalized treatment plan, providing regular check-ups, and making adjustments to the treatment plan as needed. Regular communication with the healthcare team is essential for managing blood sugar, preventing complications, and improving overall health.
Educating Patients
Patient education is a cornerstone of effective diabetes management, particularly during the honeymoon phase. Individuals newly diagnosed with type 1 diabetes need to learn about the disease, its treatment, and the importance of self-management. This education covers a wide range of topics, including insulin administration, blood glucose monitoring, carbohydrate counting, healthy eating, and exercise. Diabetes educators and healthcare professionals play a vital role in providing this education and answering questions. Ongoing education is crucial to help individuals adapt to changes, manage challenges, and maintain good blood sugar control. Regular follow-ups and refresher courses can help reinforce knowledge and address evolving needs.
Psychological and Emotional Support
Living with type 1 diabetes can be emotionally challenging, and it is important to address the psychological and emotional aspects of the disease. During the honeymoon phase, individuals may experience a mix of relief, hope, and anxiety. The sudden changes in blood sugar levels, insulin dosages, and lifestyle can be stressful. Psychological support, such as counseling or support groups, can help individuals cope with these emotional challenges. Mental health professionals can provide strategies to manage stress, anxiety, and depression. Building a strong support system, including family, friends, and other people with diabetes, is also vital for emotional well-being. Taking care of mental health is just as important as physical health.
Coping with the Honeymoon Phase
Coping with the honeymoon phase requires a proactive and adaptable approach. It’s essential to embrace self-management skills, including regular blood glucose monitoring, insulin adjustments, and healthy lifestyle choices. Individuals should be prepared for potential fluctuations in blood sugar levels and be ready to make changes to their treatment plans as needed. Staying informed about diabetes management through education and resources is also crucial. By actively managing their diabetes, individuals can maintain good blood sugar control, prevent complications, and improve their overall quality of life. It’s also beneficial to have a support system for emotional and mental health.
Staying Positive
Maintaining a positive attitude is essential for managing type 1 diabetes, especially during the honeymoon phase. Focusing on the positives, celebrating small achievements, and staying hopeful can improve emotional well-being and motivation. Practicing self-care, such as getting enough sleep, eating a balanced diet, and engaging in activities you enjoy, can help reduce stress and improve mental health. Joining a support group or connecting with other people with diabetes can also provide encouragement and a sense of community. Positive thinking and resilience can help you navigate the challenges of the honeymoon phase and live a fulfilling life with diabetes.
Long-Term Diabetes Management
Managing type 1 diabetes is a lifelong commitment that extends beyond the honeymoon phase. Long-term management includes maintaining consistent blood sugar control, regular medical check-ups, and making healthy lifestyle choices. Individuals need to adhere to their insulin regimen, monitor blood glucose levels regularly, and make dietary and exercise adjustments. Understanding the long-term risks and complications of diabetes, such as heart disease, kidney disease, and nerve damage, is also important. By staying proactive, seeking medical advice, and making informed decisions, individuals can minimize the risk of complications and enjoy a healthy and active life.
Preventing Complications
Preventing complications is a primary goal in long-term diabetes management. Maintaining stable blood sugar levels is crucial for reducing the risk of diabetes-related complications. Regular eye exams, kidney function tests, and foot checks are essential for early detection of potential problems. Managing blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and weight are also important for overall health. Making healthy lifestyle choices, such as a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking, can help protect against long-term complications. Regular medical check-ups and screenings can help detect and manage any complications that may arise, helping to live a long and healthy life.
Regular Check-ups
Regular check-ups with healthcare providers are crucial for managing type 1 diabetes effectively, both during and after the honeymoon phase. These check-ups typically include blood sugar monitoring, A1C tests (to assess average blood sugar levels over time), and screenings for diabetes-related complications. Healthcare providers can evaluate overall health, review treatment plans, and make adjustments as needed. Regular check-ups also provide an opportunity to address any concerns, ask questions, and receive ongoing education and support. Following a schedule of regular check-ups can help individuals stay on top of their diabetes management and maintain their overall health and well-being.
